Assembler, Compiler and Interpreter
- In computer science, an assembler is a program that turns assembly language into machine code.
- An assembler is a program that takes basic computer instructions and converts them into a pattern of bits that the computer’s processor can use to perform its basic operations. Some people call these instructions assembler language and others use the term assembly language.
- For example, a “Load” instruction causes the processor to move a string of bits from a location in the processor’s memory to a special holding place called a register. Assuming the processor has at least eight registers, each numbered, the following instruction would move the value (string of bits of a certain length) at memory location 3000 into the holding place called register 8: L 8,3000
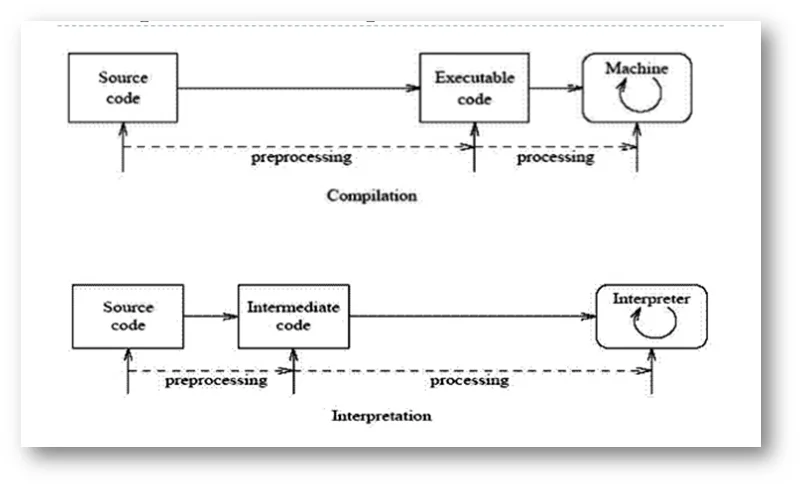
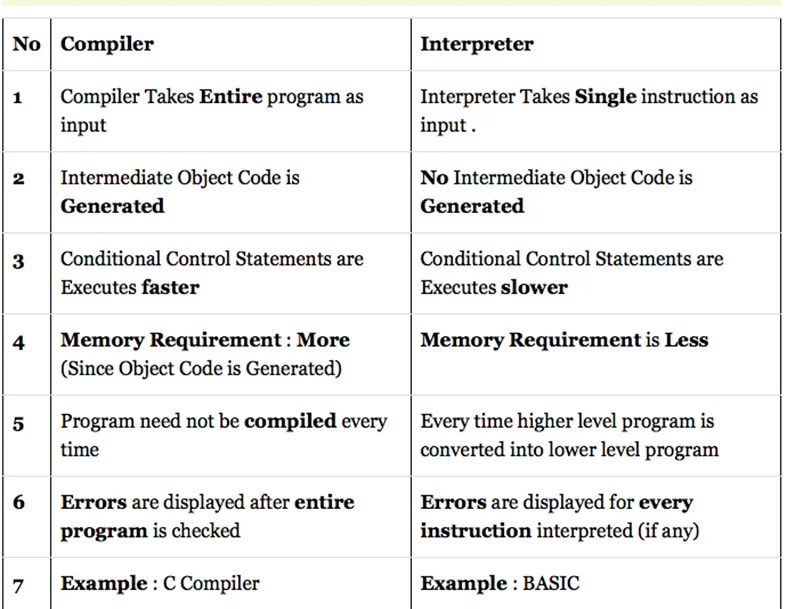
- An interpreter is a computer program that is used to directly execute program instructions written using one of the many high-level programming languages.
- The interpreter transforms the high-level program into an intermediate language that it then executes, or it could parse the high-level source code and then performs the commands directly, which is done line by line or statement by statement.
- A compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language into another programming language.
- The name compiler is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower-level language to create an executable program.
- The first-generation languages, or 1GL are low-level languages that are machine language.
- The second-generation languages, or 2GL are also low-level languages that generally consist of assembly languages.
- The third-generation languages, or 3GL are high-level languages such as C.
- The fourth-generation languages, or 4GL are languages that consist of statements like statements in a human language. Fourth generation languages are commonly used in database programming and scripts.
- The fifth-generation languages, or 5GL are programming languages that contain visual tools to help develop a program. A good example of a fifth-generation language is Visual Basic.